[navigation]
TL;DR:
- Background subtraction can be implemented with many approaches, including running Gaussian average, temporal median filter, kernel density estimation, etc.;
- This feature is popular in live streaming, dating apps, video conferencing, and othe domains;
- In practice, developing background replacement technology from scratch is hard, so developers often use open-source libraries (e.g. OpenCV) or commercially available software development kits (e.g. Face AR SDK).
Background Subtraction: How It Works Technically
Background subtraction (BSM) is a computer vision technique used to detect moving objects in video. It works by comparing the current frame to a reference background frame to spot differences.
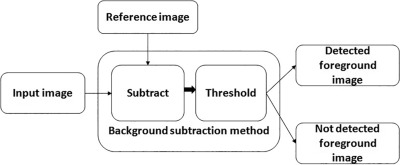
In simple terms, BSM analyzes video frames, isolates potential foreground objects, and checks them against a “no-object” frame. Differences between frames are measured and stored in a distance matrix. A threshold is a decision boundary applied to the frame difference. If the difference exceeds this threshold, the pixels (or frame areas) are classified as foreground. It becomes defined by analyzing the first several fragments of video content.
The illustration below shows the step-by-step background subtraction process:
Over the last two decades, the BSM technique has greatly evolved, and now it includes multiple approaches designed to solve challenge-specific problems that background subtraction deals with. Here are the most common methods:
- Running Gaussian average
- Temporal median filter
- Mixture of Gaussians
- Kernel density estimation (KDE)
- Sequential KD approximation
- Cooccurrence of image variations
- Eigenbackgrounds.
Let’s discuss the 2 most widespread approaches: Running Gaussian average and temporal median filter.
Key Takeaways:
- Background subtraction is all about comparing frames. If the difference passes a threshold, it’s flagged as movement.
- At its core, BSM gives apps the power to “see what’s new” in a video. That’s the foundation for popular features like background blur, replacement, and AR effects that keep users engaged.

Foreground Masks: From Detection to Object Isolation
When frame differences are spotted through background subtraction, the system produces a foreground mask. This is a binary image where:
- Foreground (moving objects) = white pixels
- Background = black pixels
The mask acts like a stencil. By applying it to the original frame, the algorithm can:
- Isolate objects (e.g., a person in a video call or any AR try-on experiences)
- Replace backgrounds with images, videos, or effects
- Track movement for surveillance, fitness, robotics, and other apps
- Enhance AR experiences by adding virtual objects or filters
Creating a clean mask usually involves:
- Frame differencing (detect pixel changes)
- Thresholding (marking changed pixels as foreground)
- Noise reduction (removing small artifacts with morphological operations)
- Refinement (smoothing edges and handling shadows)
This foreground mask is the core output of background subtraction, the tool that makes background removal, blur, or replacement actually possible in real-world apps.
Key Takeaways:
- The foreground mask is a binary map that needs careful refinement (noise cleanup, edge smoothing, shadow handling) to work well in production.
- This mask is what lies behind background blur, replacement, and AR effects. The cleaner the mask, the more seamless and professional the user experience feels.
 Background subtraction and AR filters
Background subtraction and AR filters
Core Challenges of Background Extraction
Uncertainty Treatment
Modern background subtraction algorithms are much better than those from 15 years ago, but undefined or ambiguous values still cause issues. For example, shadows are often misclassified as foreground, reducing accuracy.
Filling the Gaps
Many algorithms struggle with undefined pixels, creating holes in the background model. These gaps can cause false positives or negatives. Image reconstruction can reduce errors, but it doesn’t fully solve the pixel-gap problem.
Postprocessing
Depth- and color-based models often generate small blobs, thin edges, or noisy artifacts. Accuracy drops further with illumination changes, reflections, or dynamic backgrounds. Sensors like Kinect detect large objects well, but lighting and background dynamics can still lead to misclassification and postprocessing errors.
Mitigation Strategies: Tackling Common Background Subtraction Issues
Background subtraction is powerful, but it’s not without its flaws. Here’s how developers and SDKs handle some of the trickiest challenges:
Shadows and Ambiguous Pixels
Shadows can be a pain, as dark areas often get mistaken for foreground objects. OpenCV tackles this with built-in shadow detection, so shadows stay in the background. Another trick is to switch from RGB to YUV color space. The Y channel’s consistency under varying light conditions makes it easier to tell moving objects apart from shadows.
Dynamic Backgrounds
Scenes with subtle motion (like waving trees or flickering screens) can confuse a naive algorithm. Adaptive learning rates help here. The background model updates gradually, letting the algorithm learn what’s “normal movement” without flagging every tiny change as foreground.
Bootstrapping and Initialization
Getting the initial background model right is crucial. If the first few seconds of video include moving objects, the algorithm can start off “dirty.” Using a running median filter during the first few frames smooths out transient objects and creates a more stable baseline.
Camera Motion
A moving camera adds another layer of complexity. Without compensation, the algorithm will think the entire frame is moving. Global motion compensation (GMC) aligns frames based on the dominant motion in the scene. This lets the algorithm ignore camera movement and focus on the actual moving objects.
OpenCV vs Commercial SDKs
This is less of an issue with background subtraction as a feature and more about its implementation in a specific project.
OpenCV is a free, open source computer vision library that helps in creating various related software: image recognition, background replacement, access control, etc. There are also paid proprietary software development kits (SDKs) - premade modules that can be integrated into an app and perform certain functions. Some companies prefer building their own solutions based on OpenCV, while others opt for SDKs. When should you choose which?
Firstly, OpenCV is just a foundation, while SDKs are feature-complete products. This means that if you have the capabilities, expertise, time, and budget for a unique custom solution, the library is a good choice. It is also the only option when there is a noticeable lack of SDKs in your niche (e.g. with self-driving vehicles). Otherwise, go for premade modules.
Secondly, OpenCV provides lower image quality by default, as it uses a "one-size-fits-all" code for iOS, Android, and Web. SDKs usually are platform-specific and optimized. This makes them better for scalability.
Thirdly, OpenCV is based on object recognition algorithms. While solid, they take second place to modern neural networks that do the same job better. In the case of background replacement, SDKs are much more accurate as a result.
Finally, SDKs have other useful features. Banuba Face AR SDK, for example, can place AR masks, color filters, virtual makeup, and do a lot of other things.
Summing up, OpenCV is better when you need a foundation for a complex custom product that you have time and money to develop. An SDK is better to quickly launch a feature-rich app
Read more about it in a dedicated article.

How We Tested Background Subtraction
To evaluate background subtraction performance and demonstrate its capabilities, we conducted hands-on tests using both custom algorithms and the Banuba AR SDK. Our testing methodology ensured reliable, real-world results across devices and platforms.
Observations & Engineer Insights
Banuba SDK: Delivered low-latency, high-accuracy masks across mobile and web platforms.
“Integration was seamless. We could see real-time background effects running smoothly on both iOS and Android devices without any noticeable lag.” — Anna, AR Engineer
OpenCV Custom Models: Worked well in controlled scenarios but required tuning for complex or dynamic backgrounds. Our test used the MOG2 algorithm with a history of 500 frames and a varThreshold of 16.
“Custom pipelines gave us flexibility, but lighting changes and shadows were challenging. It needed careful parameter adjustments to avoid artifacts.” — Mark, Computer Vision Developer
- Device Dependency: The speed and smoothness of background subtraction depended significantly on device GPU, particularly for Android users.
- Lighting & Shadows: Dynamic lighting, reflections, and shadows still caused small artifacts, confirming the need for mask refinement and post-processing.
To implement background subtraction in your app, follow these examples:
Key Takeaways:
- SDKs simplify integration and maintain high performance across platforms.
- Custom solutions provide flexibility but require more development time, tuning, and expert input.
- Visual and quantitative testing confirms SDKs as a fast, reliable path for integrating background subtraction features.
How Brands Subtract Backgrounds from Images: Use Cases
Background subtraction is a thriving computer vision technology adopted by social media, entertainment, video conferencing, live streaming, and more.
 Background subtraction
Background subtraction
Video chat & video conferencing
Apps like WhatsApp, Viber, Skype, and FaceTime use background subtraction to:
- Replace static filters with animated or custom virtual backgrounds
- Enhance immersive video communication
- Retain users with frequent, on-demand feature updates
- Focus on humans while replacing real-life backgrounds with blur, 3D environments, or custom images
- Add interactive animation effects
- Boost privacy for calls, live streaming, and AR conferencing
- Include 360° backgrounds for marketing or educational experiences
Live streaming & social media
Content creators on YouTube, Twitch, Facebook, TikTok, and beyond use background subtraction to:
- Enable immersive content creation for influencers and other users
- Customize on-camera appearances without a green screen
- Broadcast with branded, animated, or game-related backgrounds
- Save space and setup time compared to traditional chroma key setups
- Increase engagement via recommendation algorithms

Dating apps
Video dating has surged post-Covid. Dating apps like Bumble and Hinge leverage background subtraction to:
- Improve user privacy by hiding real backgrounds
- Make first meetings safer and more comfortable
- Boost user acquisition and retention through engaging features

Video editing
Mobile video editors now include background subtraction to:
- Replace green screens with custom backgrounds
- Create professional-looking videos without studio equipment
- Enhance engagement with interactive or branded visual effects
Traffic monitoring & surveillance
Background subtraction helps cities and security teams see what’s moving. It can:
- Track cars, bikes, and pedestrians in real time
- Spot traffic jams or accidents quickly
- Keep an eye on public spaces for safety and analytics
 Source
Source
Smarter streets start with smarter vision. Background subtraction lets traffic systems “see” vehicles, lane occupancy, and queues in real time. The payoff? A city that dynamically adjusts lights saw 20% faster commutes and 15% less fuel wasted at intersections.
Pose estimation & human tracking
In fitness, gaming, and AR/VR, background subtraction isolates people from their surroundings. This lets apps:
- Track body movements and poses accurately
- Overlay digital elements on users in real time
- Enable smarter training, interactive games, or AR experiences
 Source: idiap.ch
Source: idiap.ch
Content-based video coding for compression efficiency
Beyond visible effects, background subtraction also supports smarter video compression through content-based video coding (CBVC). Instead of treating every pixel equally, CBVC uses foreground masks to tell encoders which regions matter most.
This enables apps and platforms to:
- Allocate higher quality to dynamic foreground regions (like a speaker’s face)
- Compress static background regions more aggressively
- Lower bandwidth use while keeping the experience smooth
- Deliver smoother real-time streaming in low-bandwidth environments
- Optimize cloud storage and distribution costs for recorded videos
By combining object isolation with compression logic, background subtraction ensures that video platforms aren’t just more engaging but also faster, leaner, and more efficient.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
If you’ve ever wondered how robots “see,” background subtraction is your answer. It’s like giving a robot an attention filter: it knows what’s moving and what’s part of the scenery. Here’s what it powers:
- Navigation: Accurately detect and avoid obstacles in its path.
- Human-Robot Interaction: Track humans in the workspace so collaboration stays safe.
- Object Manipulation: Pick and sort objects on a conveyor like a pro.
- Situational Awareness: Help drones and autonomous vehicles understand what’s moving in a scene, not just the background.
Key Takeaways:
- Background subtraction powers video calls, streaming, and social content without green screens, while boosting privacy and engagement.
- Dating apps, video editors, and AR/VR platforms use it to create safe, professional, and interactive experiences for users.
- Cities and security teams rely on it to monitor movement, track traffic, and analyze public spaces in real time.
- Foreground masks also help compress video smarter, reducing bandwidth and storage needs while keeping quality high.

How to Empower Your App with Background Subtraction
You can empower your app with background subtraction in two main ways:
- Build it from scratch
- Use a ready-made SDK
Let’s break down both options.
1. Custom Functionality Development
Building from scratch is ideal for medium to large companies with an in-house R&D team experienced in neural networks and computer vision—or a tech-driven startup with IT resources.
Benefits:
- Full control over development
- Precise accuracy tailored to your product
- Potential to patent your background subtraction technology
Challenges:
- Expensive: US-based computer vision engineers average $105K/year
-
- Time-consuming: developing an MVP can take up to 12 months
If you don’t have in-house development resources, you can hire an outsourcing technology partner to build either an MVP a or a full-fledged solution. This option is still pricey and risky since you should adjust for multiple factors like the time to choose a partner, product discovery sessions, validate a vendor’s background and expertise, etc.
Ready-Made SDK
No in-house R&D? Tight timeline? A pre-made SDK gets you up and running quickly. It’s a ready-made package with everything you need to drop background subtraction into your app. Make sure to check:
- Platform (Android, iOS, Win, Mac, Web) and device compatibility
- General feature set
- Performance and stability
- Real-time background subtraction capabilities
- Supported background types (blurred, static picture, GIF, video, 3D environment)
- Customer service quality
- Trial period conditions (e.g. Banuba offers 14 days of free trial)
- Price and subscription models.
Take Banuba Background Remover API, for example. Designed by our professional in-house R&D team, we have a unique efficient background extraction technology.
A key advantage is our performance. The Banuba AR SDK offers:
- Low latency: The processing is real-time and device-based, ensuring ultra-low latency. Photo processing takes less than 1 second.
- Accuracy: It provides industry-leading segmentation accuracy, avoiding pixelated borders and other visual artifacts.
- Low GPU load: The technology is highly optimized to minimize battery drain, running efficiently on mobile GPUs.
- High FPS: Even older smartphones stay responsive, thanks to the SDK’s 30 FPS real-time engine.
The core features of Banuba’s technology include:
- Multiple background modes and effects blur, static images, 3D environments, etc)
- Portrait-to-landscape modes
- Still image and video content support
- Both real-time and post-processing availability
- iOS, Android, and Unity cross-platform support
- Multi-browser compatibility supporting Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Edge, Opera)
- 14-day free trial to test the technology inside and out.
Key Takeaways:
- Apps gain background subtraction through custom development or by leveraging an existing SDK.
- Building from scratch gives full control and custom accuracy but is costly and time-consuming.
- SDKs are quick to integrate, work across platforms, and deliver high accuracy with low latency.
- Ready-made SDKs often include multiple background modes, Face AR, AR Try-On hubs, real-time effects, and are trusted by major brands.

Wrapping Up
Background subtraction, object detection, and AR background remover features are now widely used across social media, video chat, dating apps, live streaming, and conferencing.
When adding it to your app, you’ve got two paths:
- Use a ready-made SDK – Quick to integrate, low upfront cost, and packed with features. Perfect if you want to launch fast.
- Build it from scratch – Takes time and money, but gives you full control and custom accuracy. Best if you have R&D resources or a trusted outsourcing team.
Want a fast, hands-on test? Banuba’s Face AR SDK makes it easy. With a 14-day free trial, you can try our high-accuracy background subtraction and plug it into your app in just a day.

Reference List
AR Conferencing Solutions – virtual backgrounds & filters. (n.d.). https://www.banuba.com/ar-conferencing
AR Face Filters SDK iOS Android Unity for website and app. (n.d.-a). Banuba. https://www.banuba.com/facear-sdk/face-filters
AR Face Filters SDK iOS Android Unity for website and app. (n.d.-b). Banuba. https://www.banuba.com/facear-sdk/face-filters
AR Virtual Try-On Solution for ecommerce. (n.d.). https://www.banuba.com/solutions/e-commerce/virtual-try-on
Arsenova, A. (2023, November 27). Virtual background for video conferencing: Full guide [2024]. https://www.banuba.com/blog/virtual-background-for-video-conferencing
Arsenova, A. (2024, December 3). Real-time background subtraction in unity. https://www.banuba.com/blog/real-time-background-subtraction-in-unity
Butcher, M. (2018, November 28). Banuba raises $7M to supercharge any app or device with the ability to really see you. TechCrunch. https://techcrunch.com/2018/11/26/banuba-raises-7m-to-supercharge-any-app-or-device-with-the-ability-to-really-see-you/
Kilic, A. (2024, May 9). Council Post: GPUs: the engine behind AI evolution. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/05/09/gpus-the-engine-behind-ai-evolution/
Krasko, A. (2025a, February 3). Banuba SDK vs OpenCV: a Detailed Comparison. https://www.banuba.com/blog/banuba-face-ar-sdk-vs-opencv-the-detailed-comparison
Krasko, A. (2025b, September 12). How augmented reality filters empower dating Apps. https://www.banuba.com/blog/how-augmented-reality-filters-empower-dating-apps
Krasko, A. (2025c, September 12). How to develop a mobile video editor app. https://www.banuba.com/blog/how-to-develop-a-mobile-video-editor-app
OpenCV: How to use background subtraction Methods. (n.d.). https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d1/dc5/tutorial_background_subtraction.html


 Background subtraction and AR filters
Background subtraction and AR filters
 Background subtraction
Background subtraction


 Source: idiap.ch
Source: idiap.ch